Revit in BIM revolutionized the AEC sector. As one of the most important tools in Building Information Modeling, Revit manages to streamline workflows, promotes collaboration, and ensures accurate execution of a project. Through its incorporation of state-of-the-art modeling and analytical skills, Revit empowers AEC professionals with the possibility of designing, visualizing, and managing buildings from the point of inception to completion. Let’s talk about how Revit in BIM improves project outcomes and drives innovation.
What is BIM?
BIM is a collaborative process involving the creation and management of digital representations of physical and functional aspects of a building. The models serve as shared resources for all stakeholders, which means better communication, enhanced decision-making, and optimized project execution.
Revit is one of the leading BIM tools that take these capabilities a step further by integrating advanced modeling, analysis, and collaboration features.
Key Ways Revit Improves BIM Workflows:-
Centralized Collaboration:-
Revit supports the work of numerous team members in real time on a project. Tools, such as Worksharing in Revit, enable architects, engineers, and contractors to update or edit a model simultaneously shared by all members. The implication is that centralization eliminates differences in stakeholder comprehension.
Benefits:
- Improved coordination across disciplines.
- Error caused by misunderstandings is lower.
- Revisions and updates are streamlined.
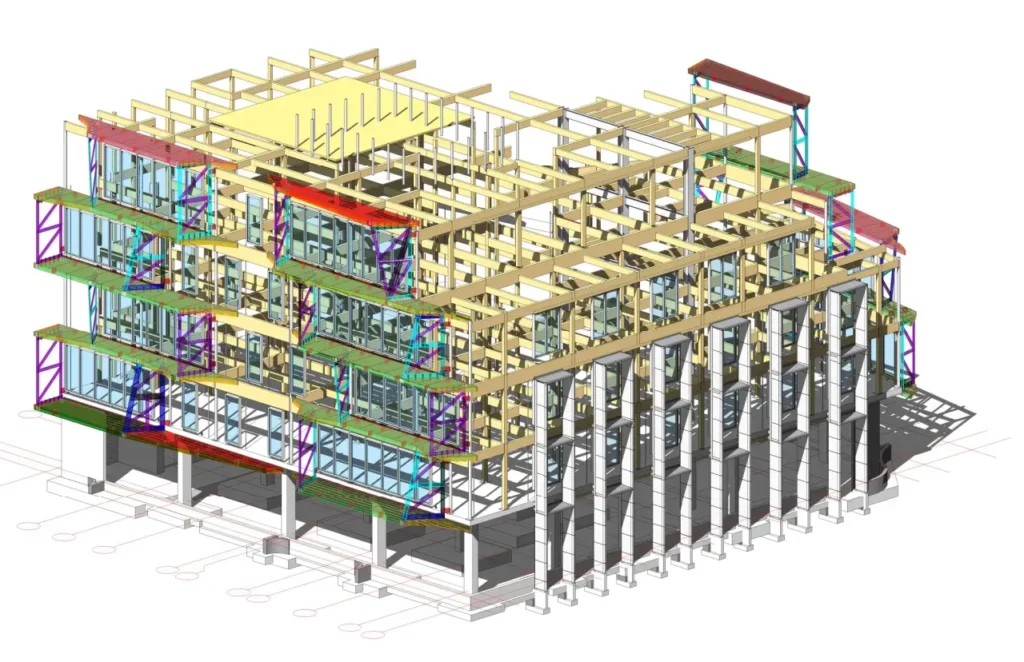
Merged 3D Modelling:-
Revit is good at making highly detailed, parametric 3D models. This software user can visualize a project in three dimensions, not with 2D drafting tools. Therefore, a better spatial understanding of design accuracy will be available.
Benefits:
- Improved design visualization for stakeholders.
- Design flaws can also be easily spotted before construction.
- Accurate clash detection and resolution.

Parametric Design:-
Revit has defined relationship capabilities in parametric modeling. Accordingly, changes in one place update the rest of the components in the model. Change in the height of a wall may change the attached roof and windows.
Advantages:
- Save much time in design modifications.
- There is uniformity in all project components.
- Freedom to experiment with many versions of the design.

Documentation and Scheduling:-
Revit automates the generation of construction documents, such as floor plans, elevations, sections, and schedules. These documents are dynamically linked to the model so that any change in design will be reflected in the documentation in real time.
Advantages:
- Less manual drafting errors.
- Faster preparation of accurate construction documents.
- Automatic generation of material takeoffs and cost estimates.
Integration with Analysis Tools:-
Revit supports interface integration with multiple analysis tools for structural analysis, energy performance, and MEP design. This helps teams optimize building performance at an early stage of the design.
Benefits:
- Energy-efficient designs through earlier analysis.
- Better structural integrity and safety.
- Streamlined MEP coordination.
Interoperability Enhancements:-
The program is meant to work well in synchronization with other Autodesk software including AutoCAD, Navisworks, and BIM 360, and with third-party applications. It uses open file formats such as IFC, allowing a seamless workflow collaboration with teams of other tools, which also operate on the BIM concept.
Benefits:
- Cross-platform collaboration.
- Data-intensively based models, where surrounding workflows are integrated.
- Long-term compatibility for future modifications.
Lifecycle Management:-
BIM is not just design; it covers the entire lifecycle of a building from conception to demolition. Revit supports facility management by giving accurate as-built models for maintenance, renovation, and decommissioning.
Benefits:
- Long-term asset management.
- Reduced operation cost by real-time data.
- Sustainability planning and optimization.
Revit in BIM in the Real World:-
Architectural Design:-
The architect uses Revit to come up with aesthetic designs with spatial accuracy. It helps create rendered images, which easily make ideas appealing to clients and hasten their approval.
Structural Engineering:-
The structural engineers use Revit to develop solid designs because they are involved with the architects and MEP teams in a manner that ensures all aspects are harmoniously integrated.

MEP Design:-
Specialized tools in the application of Revit help design efficient systems, such as mechanical, electrical, and plumbing, avoiding clashes with others that make up the construction building.
Construction Management:-
Contractors can visualize process and plan logistics, which helps determine construction costs better and reduces overruns and delays.
Conclusion:-
One of the cornerstones of BIM in modern workflows, Revit provides tools that improve collaboration, accuracy, and efficiency in all phases of projects-from design and documentation to analysis and lifecycle management-for AEC professionals looking to harness the full potential of BIM.
Whether an architect is seeking innovative designs, an engineer is assessing the structural integrity, or a contractor optimizes workflows on construction sites, Revit stands as the trusted tool bringing ideas to life with precision and confidence.
Read more on:-
For more information about engineering, architecture, and the building & construction sector, go through the posts related to the same topic on the Pinnacle IIT Blogs page.
Find out more accurately what we are going to take off in the course of applying leading new technologies and urban design at Pinnacle IIT.
Subscribe to our YouTube channel and blog websites to obtain all the up-to-date information relating to construction matters.

